
Web design and UX are constantly evolving, especially with the rapid advancements in AI and emerging technologies. Here are five web trends set to gain traction this year, trends you might want to leverage to stay competitive.
1. 3D Interactions
3D interactions are becoming a defining trend in web design, offering users more immersive and engaging experiences. These interactions go beyond flat, static visuals, incorporating real-time depth, movement, and interactivity to create a more dynamic user journey. Whether it’s a product showcase, an interactive landing page, or a full-fledged 3D web app, these elements can significantly enhance user engagement.
Why 3D Interactions Will Be Trending in 2025
Advancements in Web Technology
Modern browsers now support powerful rendering technologies like WebGL and WebGPU, making it easier than ever to bring complex 3D elements to life. Frameworks like Three.js further streamline the process, allowing developers to create stunning interactive visuals without needing to code everything from scratch. With these advancements, 3D interactions are becoming more accessible and efficient, paving the way for richer web experiences.
AI-Driven 3D Creation
The rise of AI-powered design tools is lowering the barrier to entry for 3D content creation. Designers and developers no longer need extensive 3D modelling expertise to create high-quality assets, AI can generate, refine, and even animate 3D objects with minimal effort. This shift is enabling more websites to incorporate 3D elements, making immersive interactions a standard rather than a luxury.
Immersive User Experiences
As users demand more engaging digital experiences, brands are turning to 3D interactions to stand out. Whether it’s a fully interactive product showcase, an engaging landing page, or a gamified website experience, 3D elements help capture attention and keep users engaged for longer. These interactions add depth to the web, making sites feel more dynamic and interactive rather than static and flat.
Faster Load Times
In the past, 3D content was often dismissed due to performance concerns, but that’s changing. Advances in GPU acceleration and optimisation techniques now allow 3D experiences to run smoothly without significantly impacting load times. Developers can create visually rich, interactive web elements while maintaining fast and responsive performance, making 3D interactions a viable option for more websites than ever before.
Introducing WebGL
What is WebGL?
WebGL (Web Graphics Library) is a JavaScript API that enables browsers to create interactive 2D and 3D graphics without relying on external plugins. It provides direct access to a device’s GPU (graphics processing unit), allowing for smooth, hardware-accelerated rendering of complex visuals. This makes it the backbone of many modern web-based 3D experiences, from interactive product showcases to immersive games.
You’ve likely encountered WebGL without even realising it. It powers many of the interactive experiences you use daily, from smooth transitions in Google Maps to engaging 3D animations on websites and web-based games. By leveraging a device’s GPU, WebGL enables seamless, high-performance graphics that make web applications feel more dynamic and responsive.
However, working with WebGL directly can be challenging. It requires deep knowledge of computer graphics, shader programming, and low-level rendering techniques. That’s where tools such as Three.js come in to save the day.
Three JS
Three.js is a popular JavaScript library that simplifies the process of building 3D experiences on the web. Instead of writing hundreds of lines of WebGL code to render a simple object, Three.js provides an easier way to create and manipulate 3D elements with minimal effort. It includes built-in features like lighting, shadows, physics, and animations, making it an essential tool for developers looking to add interactive 3D elements to their websites.
Three.js is widely used across industries, appearing on high-profile websites like Apple’s Vision Pro landing page, where it helps create smooth, visually rich 3D animations. From dynamic product showcases to interactive storytelling experiences, Three.js has become the go-to library for web developers looking to harness the power of WebGL without the steep learning curve.
You can see the full potential of Three.js in action on its official demo page, where you’ll find a variety of interactive 3D scenes, animations, and effects that showcase what’s possible with the library.
What If I’m Not That Technical? Are There Design-Friendly Tools?
For designers or those looking for a more intuitive, no-code approach, tools like Spline provide a way to create real-time 3D interactions without needing deep technical expertise. Unlike WebGL, which requires programming knowledge, Spline offers a visual interface that allows designers to build and animate 3D objects directly, opening up new possibilities for web design without writing code. See for yourself by interacting with the demo below.
Interested in seeing more demos? Check out the official Spline demo library here.
2. AI-Generated Images and Videos
AI-generated images and videos are visual content pieces created using artificial intelligence algorithms. These tools use machine learning models, like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), to analyse vast amounts of data and then generate realistic or artistic images and videos based on that data. For example, you can input a text description of what you’re after, and the AI will create a unique image or video that matches the input. These AI tools have made it possible to create everything from realistic landscapes to entirely new visual art without the need for traditional photography or video production.

(AI generated image)
Is It Legal?
The legal status of AI-generated images and videos can be a gray area. Currently, the ownership of AI-generated content depends on various factors, including the tool used and its licensing agreement. In many cases, the person using the tool may own the content, but this can vary based on the terms and conditions of the specific platform. There are also copyright concerns around whether AI-generated works can be copyrighted, as copyright law traditionally requires human authorship. As the use of AI in content creation grows, we may see more defined rules and regulations around ownership and usage rights.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Benefits
- May enhance creativity and improve efficiency: AI can quickly generate unique images or videos, saving time for content creators and designers. It allows for exploration of creative ideas without having to start from scratch.
- Cost effective: For businesses that need large volumes of content, AI tools can generate images or videos without the need for professional photographers or videographers, which can be expensive.
- Customisation: Many tools allow for input adjustments, giving users the ability to refine and control the generated content to match specific needs or preferences.
Drawbacks
- Quality Control: While AI can generate impressive content, it may not always meet the quality expectations of professional creatives. The generated images or videos might require refinement or editing to be polished.
- Presents ethical concerns: The use of AI in content creation raises questions around authorship, authenticity, and originality, particularly if AI tools replicate or modify existing works.
- Copyright issues – As discussed earlier, the legal status of AI-generated content is still unclear, and there may be complications regarding ownership and usage rights, especially when commercialising the content.
AI-generated images and videos are rapidly becoming a major trend in web design and content creation, offering both opportunities and challenges. As these tools evolve, they may drastically change how visual content is produced and consumed online.
3. Dark Theme
Dark theme (or dark mode) is a user interface design choice where the background is primarily dark, usually black or dark gray, with lighter text and icons. This design approach is a popular alternative to the traditional light theme, which uses white or light backgrounds with dark text. Dark theme is often praised for its sleek, modern look, and it’s widely adopted across operating systems, apps, websites, and social platforms. According to this LinkedIn article, dark mode is used by 81.9% of 2,500 Android users on their phones, in apps, and other situations. 9.9% alternate between the light and dark settings, showing significant amount of users utilising dark mode of light.
Why Is It On the Rise?
But, why is dark mode on the rise? What benefits does it provide? Dark theme has gained significant traction in recent years for several good reasons.
User Preference and Comfort
Many users find dark themes easier on the eyes, especially when using devices in low-light environments. It reduces the amount of bright light emitted by screens, which can cause eye strain or disrupt sleep patterns, particularly in the evening. In 2024, nearly 82% of smartphone users use dark mode (Earth Web)!
Trend in Operating Systems
Operating systems, including Windows 10, macOS, Android, and iOS, have embraced dark mode as a default or optional setting. This trend has further pushed the popularity of dark themes across apps and websites. Users now expect dark mode to be available across devices and applications, making it a key part of the overall user experience.
Aesthetic Appeal
Dark themes offer a stylish and contemporary look, which many brands are adopting to appear more modern or align with current design trends. The contrast between bright and dark elements can make websites and apps look more visually striking and polished.
Battery Life Improvements
On OLED and AMOLED screens, dark themes can help save battery life. This is because black pixels on these screens consume less power, making dark themes not just visually appealing but also more energy-efficient. With AMOLED screens in particular, dark mode can save up to 63% on battery life (Night Eye).
Other Considerations
- Accessibility: While dark themes offer benefits for some users, it’s important to consider accessibility. For example, people with certain visual impairments might find dark themes harder to read due to the low contrast between text and background. It’s important to ensure that contrast levels are high enough for readability.
- Customisation: The rise of dark themes has led to more customisable UI options, allowing users to toggle between light and dark modes based on their preferences. This level of control over the user experience is part of the broader trend of personalised web experiences.
- User adoption: Many major social media platforms, including Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook, offer dark theme options, and their popularity on mobile devices has led to greater adoption across websites and web applications.
Dark theme isn’t just a passing trend, it’s become a standard user experience preference across devices and platforms, driven by practical benefits like reduced eye strain, battery savings, and aesthetic appeal. As dark themes continue to gain popularity, we’re likely to see more websites and apps integrate them as a default option, with customisation features to give users more control over their interface.
4. Accessibility
Accessibility, in the context of web design and development, refers to the practice of creating websites, applications, and content that can be accessed and used by all people, including those with disabilities. This includes users who may have visual impairments, hearing loss, limited motor skills, or cognitive disabilities. The goal of accessibility is to ensure that everyone, regardless of their abilities, can interact with digital content in a meaningful and functional way.
Key Accessibility Standards You Need to Know
- WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines)
- ADA Compliance (Americans with Disabilities Act)
For an internationally compliant website, WCAG is the most crucial standard, as it’s widely recognised and adopted across the globe, with many countries aligning their laws and guidelines with it. It ensures accessibility for users with disabilities, regardless of location. ADA compliance, on the other hand, is more specific to the U.S. and apply primarily to U.S.-based organisations or those working with the U.S. government. However, they are often referenced globally, particularly when U.S. businesses are concerned about legal compliance. For international compliance, it’s sufficient to focus primarily on WCAG, as many countries either have their own accessibility regulations aligned with it or use WCAG as a standard for their own guidelines.
Introducing WCAG
One of the key frameworks for implementing accessibility in design is the WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines), developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). WCAG provides comprehensive guidelines and success criteria to ensure digital content is accessible to a wider audience. These guidelines are organised into four principles:
- Perceivable: Information and UI components must be presented in ways that users can perceive, such as providing alternative text for images or ensuring content is compatible with screen readers.
- Operable: UI components and navigation must be operable through different input methods, like keyboards, voice commands, or other assistive technologies.
- Understandable: Content and navigation must be easy to understand and predict. This includes providing clear instructions, error messages, and consistent layouts.
- Robust: Content must be robust enough to work with current and future technologies, ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies and browsers.
By following these guidelines, designers and developers can create websites that cater to a broader range of users, improving the overall accessibility of digital content. Learn more about these four principles here.
Websites like WebAIM offer valuable tools, such as their contrast checker, to help improve WCAG compliance and enhance web accessibility by ensuring that your site’s design meets the necessary color contrast ratios for readability.

(WebManics’ contrast checker passes with flying colors!)
Introducing ADA Compliance
ADA Compliance refers to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a landmark U.S. law passed in 1990 aimed at preventing discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including digital spaces. While the ADA originally focused on physical access, it has been interpreted to include digital accessibility, meaning that websites and digital services must be accessible to people with disabilities, including those with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments.
Why is ADA Compliance Important?
ADA compliance is important not just for legal reasons but also for fostering inclusivity and ensuring that everyone, regardless of ability, can access and navigate your website. In recent years, there has been an increase in lawsuits and legal action against companies whose websites are not accessible, as disabled users seek to exercise their rights under the ADA. By adhering to ADA standards, businesses can avoid legal challenges, enhance their brand reputation, and ensure they are serving all potential customers.
How ADA Compliance Relates to Web Accessibility
While the ADA does not specify exact technical guidelines for digital accessibility, its broad mandate has been interpreted to require websites to be usable by individuals with disabilities. To meet these requirements, businesses often turn to guidelines like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which offer detailed standards for making websites accessible.
Key Elements of ADA Compliance
To ensure ADA compliance, a website should address a variety of accessibility factors, including:
- Keyboard navigation: Ensuring the site can be fully navigated with a keyboard for users with motor impairments.
- Alternative text (better known as alt text): Providing alt text for images, videos, and other media so that screen readers can interpret them for users with visual impairments.
- Colour contrast: Ensuring text has sufficient contrast with the background to aid users with visual impairments.
- Accessible forms: Making sure forms are designed in a way that is easy for users with disabilities to complete.
- Responsive design: Ensuring websites are usable on all devices, which benefits users with varying abilities and needs.
How to Achieve ADA Compliance
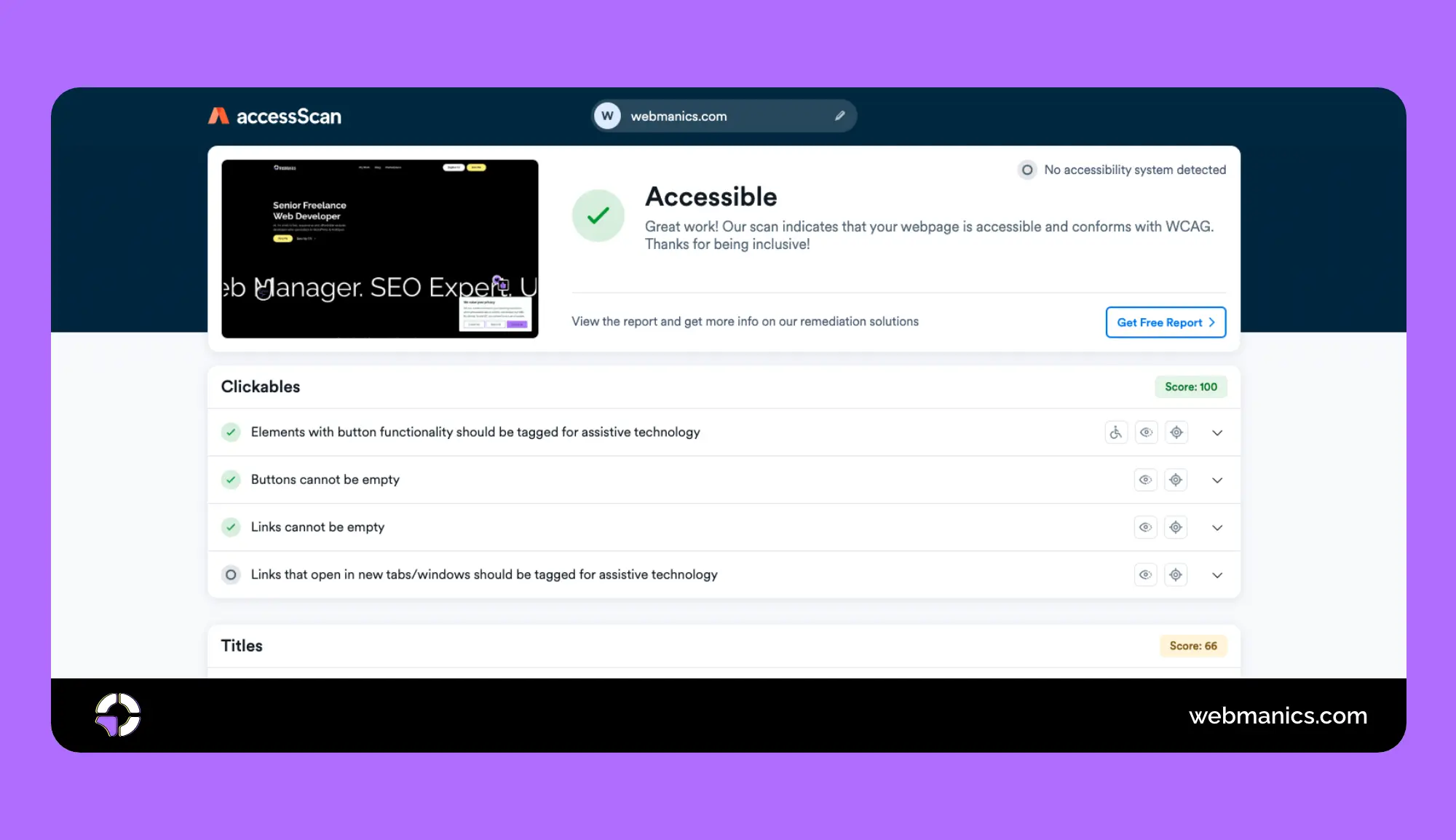
The first step is auditing your site’s current accessibility. Tools like Accessibe’s AccessScan can help you assess its status.
Upon scanning, you will receive one of three assessment results:
- Non-compliant: Your site needs significant improvements.
- Semi-compliant: Almost there, but not fully compliant yet.
- Accessible: Fully compliant, great work!
If you’re categorised as non-compliant or semi-compliant, or even if you’re fully compliant but looking for further enhancements, don’t worry. The audit tool provides a detailed list of categories and areas where improvements can be made.
How to Implement Accessibility in Development
When it comes to implementing accessibility in development, there are various technical solutions to help ensure that digital content is accessible. Some essential steps include:
Use of ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) Labels
ARIA labels help developers make dynamic content accessible to screen readers. These labels provide additional information about the content for users with visual impairments. For example, a button or link can be given an aria-label attribute to describe its function when the text on the button is not descriptive enough. Example:
<button aria-label="Close menu">X</button>
Semantic HTML
Using semantic HTML tags like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <nav> helps assistive technologies identify the structure of a page. It improves navigation for users who rely on screen readers, as they can easily jump to specific sections.
Keyboard Accessibility
Ensure that all interactive elements (like buttons, forms, and navigation menus) are navigable and operable using a keyboard. This is essential for users who cannot use a mouse due to physical disabilities.
Color Contrast and Text
Ensure that there is sufficient contrast between text and background colors. Poor contrast can make reading difficult for people with visual impairments, such as color blindness or low vision. Tools like the WebAIM Contrast Checker can help assess whether your color choices meet the minimum contrast ratio for accessibility.
Alt Text for Images
Always provide descriptive alt text for images, which allows screen readers to describe the content of images for users with visual impairments. The alt text should be succinct but descriptive of the image’s purpose or meaning. Example:
<img src="logo.png" alt="Company logo with text 'WebManics'">
Focus Indicators
Ensure that interactive elements have visible focus indicators (such as a border or outline) when navigating with a keyboard. This helps users know where they are on the page and how to interact with elements.
Incorporating accessibility in design and development isn’t just about following guidelines or fulfilling legal requirements, it’s about creating a better, more inclusive experience for all users. By prioritising accessibility, developers and designers can help ensure that their websites are usable by people with disabilities, improving usability and providing equal access to digital content. The WCAG, ADA, and other standards provide a clear framework for ensuring accessibility, and with the right tools and strategies, accessibility can be seamlessly integrated into both the design and development process.
5. Large, Bold Typography
Large minimalistic typography has emerged as one of the most impactful design trends in recent years, and it’s continuing to gain traction in 2025. This trend is all about making a statement, creating emphasis, and guiding users’ attention to important content. The use of oversized fonts, thick weights, and strong contrasts creates a visual hierarchy that’s not only eye-catching (take our homepage as an example!) but also enhances readability and user experience.
Several factors are contributing to its rise:
- The need for visual impact: As attention spans shrink, digital content needs to grab the viewer’s attention quickly. Large typography immediately stands out, ensuring that key messages are noticed first. When used strategically, it can make headlines, CTAs, and important statements impossible to miss.
- Mobile optimisation: With mobile-first design becoming a standard, large typography offers clear and legible text, even on smaller screens. Big, bold fonts are easier to read on mobile devices and tablets, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Minimalist design: In the age of minimalism, typography has taken on a bigger role as one of the main design elements. The focus shifts from heavy imagery to typography itself, allowing brands to convey messages more directly. Large, bold type can carry the weight of the design without the need for complex graphics.
- Creativity and expression: Large typography enables designers to express creativity and reinforce brand identity. Brands are increasingly using oversized fonts to make a strong statement about their values, personality, and tone, making their websites and content more memorable.
Benefits
- Immediate attention: Large type grabs the user’s attention immediately, whether it’s a headline, tagline, or important call to action (CTA).
- Clear hierarchy: Bold fonts help establish a clear visual hierarchy, ensuring that important elements stand out and are easy to locate.
- Readability: Larger fonts are often easier to read, especially on mobile devices, ensuring your message is communicated without frustration.
- Brand identity: Bold typography allows for more creative and distinct expressions of brand personality, helping a company stand out from competitors.
Drawbacks
- Overuse can be overwhelming: If large typography is overused or applied to every element of the design, it can overwhelm the viewer and reduce its impact. Balance is key.
- Accessibility: While large text is easier to read, excessive bolding or very large fonts may still present challenges for people with certain visual impairments, so it’s important to consider legibility factors like contrast and font choices.
Large typography is more than just a trend, it’s a powerful tool for communication. As the design world shifts toward minimalist aesthetics, oversized typography continues to prove its worth by making bold statements, guiding user attention, and creating a clear visual structure. For designers, using large, bold typography is an effective way to make sure your content is seen and understood, while also elevating the user experience.
Conclusion
As we move into 2025, these web design trends are not just shaping how websites look, they’re transforming how users interact with digital experiences. From the immersive feel of 3D interactions to the practicality of AI-generated media, the web is evolving rapidly. Dark themes, large, bold typography, and enhanced accessibility standards are ensuring that design is not only visually captivating but also inclusive and user-friendly.
Staying ahead of these trends will help you create modern, engaging, and functional web experiences that resonate with your audience. As these trends continue to evolve, embracing them will be key to staying relevant and competitive in the ever-changing digital landscape.